Non -standard skin cell growth is usually called neoplasms.As the main reason for the appearance of neoplasms, experts call the effects of ultraviolet radiation.
The second cause of damage to the skin is carcinogenic.In any case of new education on the skin, it is necessary to monitor and consult with doctors - timely oncologists.
He will perform all the required diagnostic procedures.And he would recommend the next action you need to take.
Papilloma, Wart and Condyloma - all of these are the result of papillomavirus or HPV activities.The virus enters the human body and is inactive for a long time.Under the influence of causing factors, HPV activation occurs.This is reflected in the formation of soft growth on the skin and mucous membranes.
Neoplasms can exacerbate the quality of life, cells are characterized by mutting, leading to oncology.Timely diagnosis of diagnosis and papillomas on the genitals is key to a healthy and full of a woman's intimate life.
Reason -as a papilloma appearance in the mouth
The main reason for the appearance of growth in the mouth is the presence of human papillomavirus in the body.It is easy for them to be infected: the virus is sent to domestic and through personal contact (touch, unprotected sex).The main method of infection with the virus:
- Not comply with personal hygiene rules, use of brushes and dental towels;
- The household method consists of disinfection of the objects and appliances used in conjunction with the infected person;
- Personal relationships with virus carriers (kisses, oral sex, sexual relations);
- Newborn virus infections occur during the path along the birth canal of the mother, which is a HPV carrier.
The incubation period of the disease can last several years.HPV is only available by passing the test.
There are several factors that affect the activation of the virus and the appearance of symptoms:
- Frequent colds and chronic inflammation processes, decreased immunity;
- Stressful lifestyle and bad habits;
- Hormone violations;
- Taking antibiotics and long corticosteroids (hormone drugs);
- Gastrointestinal tract disease;
- Pregnancy;
- Systematic injury of the mucous membrane (using toothbrush with hard feathers, hot foods and drinks, denstionization, braces);
- Caries, periodontal disease, gingivitis.
Any papilloma that appears in the body due to HPV (human papilloma virus).Papillomas in intimate areas are a widespread phenomenon.Growth is in the thigh, in the vagina, to the experts, in the anus.Often, sexual papilloma is found in children.Neoplasms can convey it to the carrier not only the constraints, but also the physical discomfort.According to medical statistics, the genital papilloma virus is found to be almost a quarter of the population.
The mechanism of formation of papilloma in an intimate zone
In an inactive state, the human papilloma sexual virus can live in the body for a long time.Virus carriers can infect others, unaware of this.
The process of activation and growth of virus cells occurs when the body's protective force is weak.As a result, neoplasms occur.
Contrary to the widespread opinion that papilloma causes exclusive discomfort in cosmetic terms, it can also cause health problems.
HPV type
According to international standards, all neoplasms are divided into three types:
- Tame.
- Malignant.
- Precancerous.
It is important to determine the appearance of papilloma on the body.The type of neoplasm depends on the tension of the virus.
In most cases, people face harmful forms of infection, which is not harmful to health and only causes aesthetic discomfort.It is enough to get rid of such warts to forget the discomfort.
Differentiating different types of warts on the body is quite easy by comparing various photos.Each type of education is characterized by several features, knowing what is easy to suspect is a particular form of a disease.
Normal papillomas or abusive warts
The most common form of papillomavirus manifestation is a common papillomas, called warts.They are caused by some virus strains, which are easily disseminated by touch and sexual.
According to statistics, about every third person on the planet at least once in his life it touches the arrival of a regular papillomas.
There are several types of papilloma in the mouth:
- Epithelial hyperplasia - a small formation of papillae, most often formed on the language side;
- Simple (rough) papilloma appears in the sky and has a flat cone shape;
- Vulgar papilloma;
- Growth in gums is most often represented in the form of flat papilloma;
- Flat papillomas;
- Film papillomas have a fine foundation, which often causes bleeding and inflammation, if they are injured.Found on top of the tongue;
- N weblomes in the tongue;
- Sharp condylomas have a cones, interconnected and form a major damage;
- Sharp papillomas
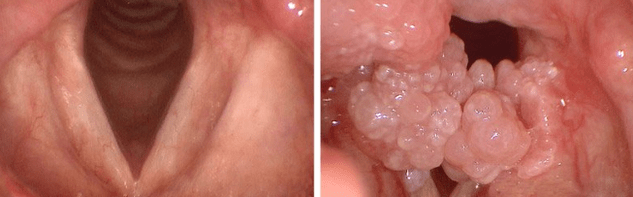
IMPORTANT!Diagnostics soon threatens the growth of papillomatous nodes on the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract.
Papillomas on the tongue and cheeks can have different shapes.Polyps on the cheeks are small soft bumps and do not cause pain.Growth in language is subject to irritation and micro grass, which can cause bleeding.
Papillomas on tonsils are often confused with laryngitis or purulent sore throat.Due to growth, swelling of the respiratory tract and vocal cords can be observed, causing difficulty breathing.
Unpleasant sensations accompany the food absorption process, even fluid.Sometimes a person suffers from the presence of a foreign body in the throat.
The appearance of papilloma in the larynx can be accompanied by voice changes, respiratory problems.While eating solid foods, mucous membranes with growth can be crushed.Red throat in children may indicate the presence of growth.Papillomatosis in children is the cause of bronchitis.
The emergence of pathological formation in the form of cones or polyps on the gums (growth of the gums) is dangerous as the mucous membranes will be injured by a toothbrush or toothbrush.Finally, this will lead to the process of inflammation and unpleasant wound infections.
Papillomavirus, in addition to skin changes, is a danger to the development of various diseases.The type of infection shows how it will develop and what is the danger.
Condyl type determination is required for:
- Identification there is a risk of rebirth of growth into malignant tumors;
- Effective treatment selection;
- Determine the type of infection.
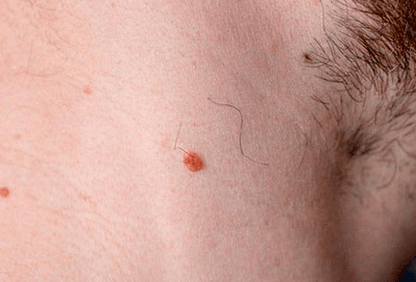
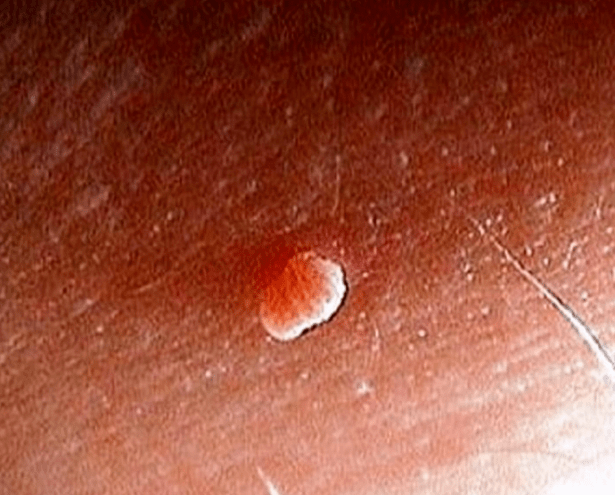
Simple
Also known as abusive or ordinary.The formation of papilloma is preceded by a slight burning sensation.
Over time, spherical growth appears, resembling a tumor.Even later, the smooth surface of the neoplasms turned into rough, and the color of the body passed darker.
Dimensions can change from 1 to 10 mm.
Often, common warts appear between the fingers and on the palm of the back.For children who are mainly moving, they can be localized to their knees.Is single and double.
Often, coarse papilloma does not pose a danger to human health, which represents benign growth.
Subanary
The name itself shows the localization of papillomas.In order not to blame them for corn, there are some marks of talking:
- Neoplasms on all signs resembling a normal warts;
- There is pain in the growth area when wearing small united shoes;
- No skin pattern, and the surface is rough.
Plantar verrucas papillomatosis mosaic that exists, when the bubble is formed near the basic formation, over time - papillomas.
In small children, plantar warts can be lost on their own.
Flat
They have oval, stretched, less round.They are characterized by slight heights - only a few millimeters stand out on the skin.The face is affected, the upper skin of the chest, sometimes the external genital organs.
The color is slightly darker than the color of the body.Nearby, the papillomas of the aircraft have the property to connect to one place, after which they become more noticeable.
Film
Warts characterized by certain feet and longitudinal forms are called threaded (acrochordus).Initially, the lower neoplasm has a small cone shape, which is then stretched.
Usually found in men and women after 40 years.They are located in the neck, in the eyelids, under the armpits, in the inguinal zone, near the milk gland.Often injured due to the presence of thin feet, which can easily damage the clothing or inaccurate movement.
Sharp
Absorbing out to resemble papillary education.They can affect both skin and throughout the group.As they grow, they are combined into one whole, forming a bright meat or pink color.
The appearance of sharp warts is provoked by sexual infections.In this case, condylomas affect the genitals, the inguinal zone, the area near the anus.
Sharp papillomas develop quickly and can occupy most of the healthy tissue in a few days.Even after successful treatment, relapse is not excluded.
Medicine has more than a hundred types of papillomavirus.About forty they are sexually transmitted, and thus affects the genitals of men and women, many types of HPV are not harmful at all, some are very dangerous and can cause oncological diseases.
Types of human papilloma viruses are common to classify the probability of oncogenic formation on the skin.Distinguish:
- Very dangerous types - 16, 18, 36, 45;
- The average type of danger is 31, 33, 35, 51, 52, 58;
- Safe type - 6, 11, 42, 43, 44.
HPV is a microorganism with up to one hundred stamps.Depending on the type that affects HPV stamps, various types of papilloma are also formed on the skin.They differ in appearance, growth rate, body location.
Some papillomatous growth is detected on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, in the bladder, in women in the vagina, and in men in the penis.
Determination of papilloma species is required to choose the most effective treatment method and to evaluate the risk of rebirth of this tumor becomes malignant.
Official medicine divides HPV into 4 groups:
- not oncogenic;
- low onkogenic;
- carry average oncogenic risk;
- characterized by high levels of carcinogenic.
Non -oncogenic, that is, not being born again into a cancerous tumor over time, as a rule, is a rough, flat, plantar papillomas.If we take a general definition of papilloma, then, translated from Latin, you can characterize it as a "tumor in the form of papilla".















